Explain How the Bacteriophage Lysogenic Cycle Is Different
The difference between lysogenic and lytic cycles is that in lysogenic cycles the spread of the viral DNA occurs through the usual prokaryotic reproduction whereas a lytic cycle is more immediate in that it results in many copies of the virus being created very quickly and the cell is. In this cycle intra-cellular multiplication of the phage results in the lysis of host bacteria resulting in release of progeny virions.

The Lytic And Lysogenic Cycles Of Bacteriophage Infection By Viral Dna Download Scientific Diagram
Also known as temperate cycle.
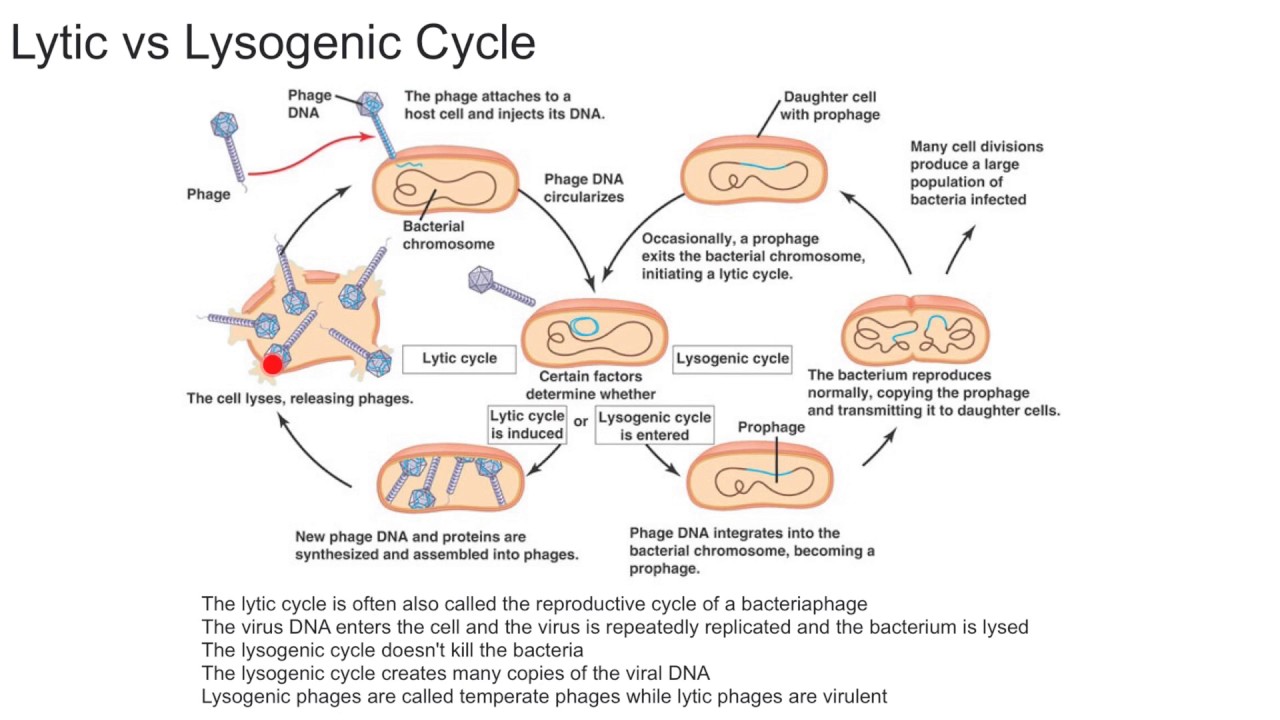
. In the lysogenic cycle the first two steps attachment and DNA injection occur just as they do for the lytic cycle. They do not have a cellular structure acellular. Lytic Cycle vs.
The viral DNA destroys DNA of the host cell halting the cells functioning in Lytic Cycle. Lysogeny or the lysogenic cycle is one of two cycles of viral reproduction. The lysogenic cycle Figure 3 sometimes referred to as temperate or non-virulent infection does not kill the host cell instead using it as a refuge where it exists in a dormant state.
This cycle takes place in the following steps. During the lysogenic cycle instead of killing the host the phage genome which is called a prophage integrates itself to the bacterial chromosome and becomes part of the host. Bacteriophages inject DNA into the host cell whereas animal viruses enter by endocytosis or membrane fusion.
Viruses can cycle through the lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle depending on several factors. 9 rows Lytic cycle comparitively more common is a method of viral multiplication wherein the virus. In the lytic cycle the DNA is multiplied many times and proteins are formed using processes stolen from the bacteria.
The key difference between lytic and lysogenic cycle of bacteriophage is that during lytic cycle of bacteriophage reproduction the bacteriophage that enters the host cell present as a separate component without integrating with the host DNA while in lysogenic cycle the bacteriophage DNA is integrated into the host DNA. In this condition the bacterium continues to live and reproduce normally while the bacteriophage lies in a dormant state in the. In the Lytic Cycle a bacteriophage infects a bacteria and kills it to release progeny virus.
Phages exhibit two different types of life cycle. A bacterial host with a prophage is called a lysogen and then the entire process in which a bacterium is infected by a temperate phage is called lysogeny. The bacteriophages can propagate in two different ways.
Lysogenic Cycle or Temperate Cycle. The key difference between lytic and lysogenic cycle is that during the lytic cycle the host cell undergoes lysis while during the lysogenic cycle the host cell does not undergo lysis straight away. This video explains the Difference between Lytic and Lysogenic cycle of BacteriophageSummary of lytic and lysogenic cycleWhat is a prophage.
Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles are two viral replication processes that can occur simultaneously. Temperate bacteriophages Lysogenic cycle Temperate bacteriophages are the bacteriophage type that use the lysogenic cycle for replication. The lysogenc cycle is one where a phage infuses its generic material into a host but instead of rapidly replicating this generic material finds its way to the hosts genetic material and infuses itself with it becoming a.
Lysogeny is characterized by integration of the bacteriophage nucleic acid into the host bacteriums genome or formation of a circular replicon in the bacterial cytoplasm. However in the lysogenic cycle viral DNA may merge with the host DNA. The lytic cycle leads to the death of the host whereas the lysogenic cycle leads to integration of phage into the host genome.
In the lysogenic cycle the DNA is only replicated not translated into proteins. The main difference between lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle is that lytic cycle destroys the host cell whereas lysogenic cycle does not destroy the host cell. Lytic cycle and Lysogenic cycle.
Difference between lytic and lysogenic cycles is that lytic cycle destroys the host cell whereas Lysogenic Cycle does not. However once the phage DNA is inside the cell it is not immediately copied or expressed to make proteins. Bacteriophages have a lytic or lysogenic cycle.
Bacteriophage exhibits two major types of life cycles. These stages include attachment penetration uncoating biosynthesis maturation and release. Following the injection of the phage DNA into the host cell it integrates itself into the host genome with the help of phage-encoded integrases where it is then termed a prophage.
Bacteriophages have a lytic or lysogenic cycle. Instead it recombines with a. In this cyclephage DNA becomes integrated with the bacterial genome and replicates with the.
Lytic Cycle or Virulent Cycle. Also known as virulent cycle. April 26 2018 Posted by DrSamanthi.
The viral DNA may however fuse with the host DNA. Bacteriophages have a lytic or lysogenic cycle. The lytic cycle leads to the death of the host whereas the lysogenic cycle leads to integration of phage into the host genome.
Viral DNA destroys the host cell DNA and arrests the cell functions in the lytic cycle. These stages include attachment penetration uncoating biosynthesis maturation and release. The lytic cycle leads to the death of the host whereas the lysogenic cycle leads to integration of phage into the host genome.
On the counterpart the Lysogenic cycle can be referred as a dormant stage of the virus where the genetic material of the virus remains intact in the bacterial genome as the legitimate part. In the former as the name suggests would lead to the death of the host bacterial cell. June 7 2012 Posted by DrSamanthi.
While the lysogenic cycle can sometimes happen in eukaryotes prokaryotes or bacteria are much better understood examples. Viruses are infectious particles that cannot multiply on their own.

The Lysogenic And Lytic Cycle Of Bacteriophages The Lysogenic And Download Scientific Diagram
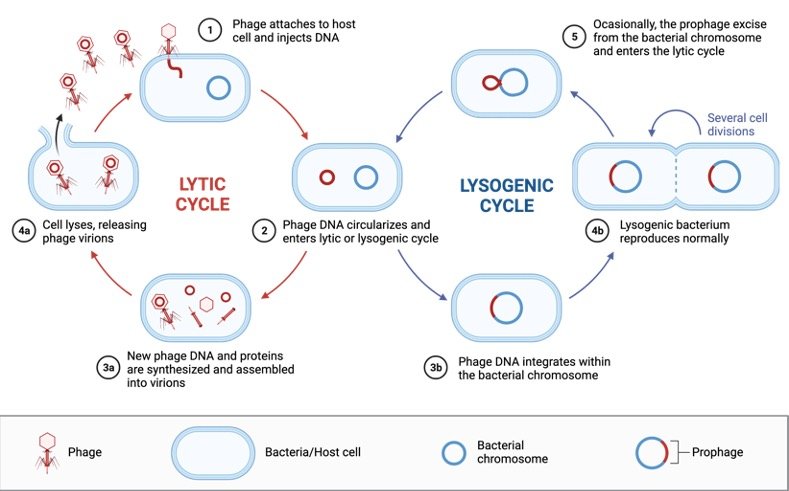
Lysogenic Cycle Definition Steps Examples I Researchtweet

Lytic Vs Lysogenic Cycle Youtube
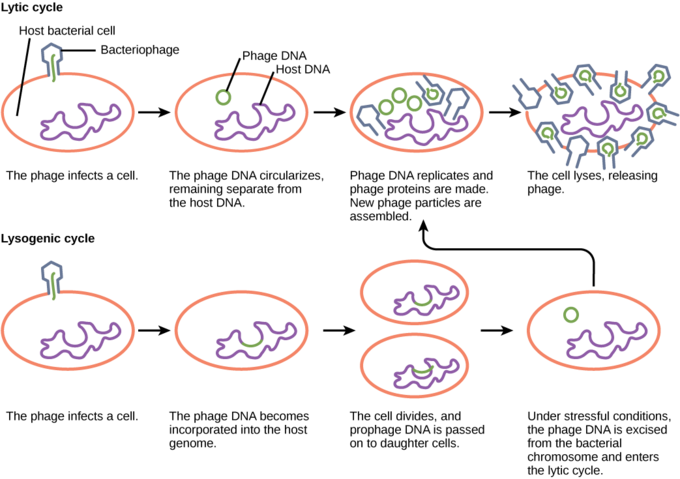
21 2b The Lytic And Lysogenic Cycles Of Bacteriophages Biology Libretexts
No comments for "Explain How the Bacteriophage Lysogenic Cycle Is Different"
Post a Comment